Vault ACL
The Vault ACL system protects the cluster from unauthorized access. It must be properly configured in order for the Vault and Nomad integrations to work.
Nomad Workload Identities
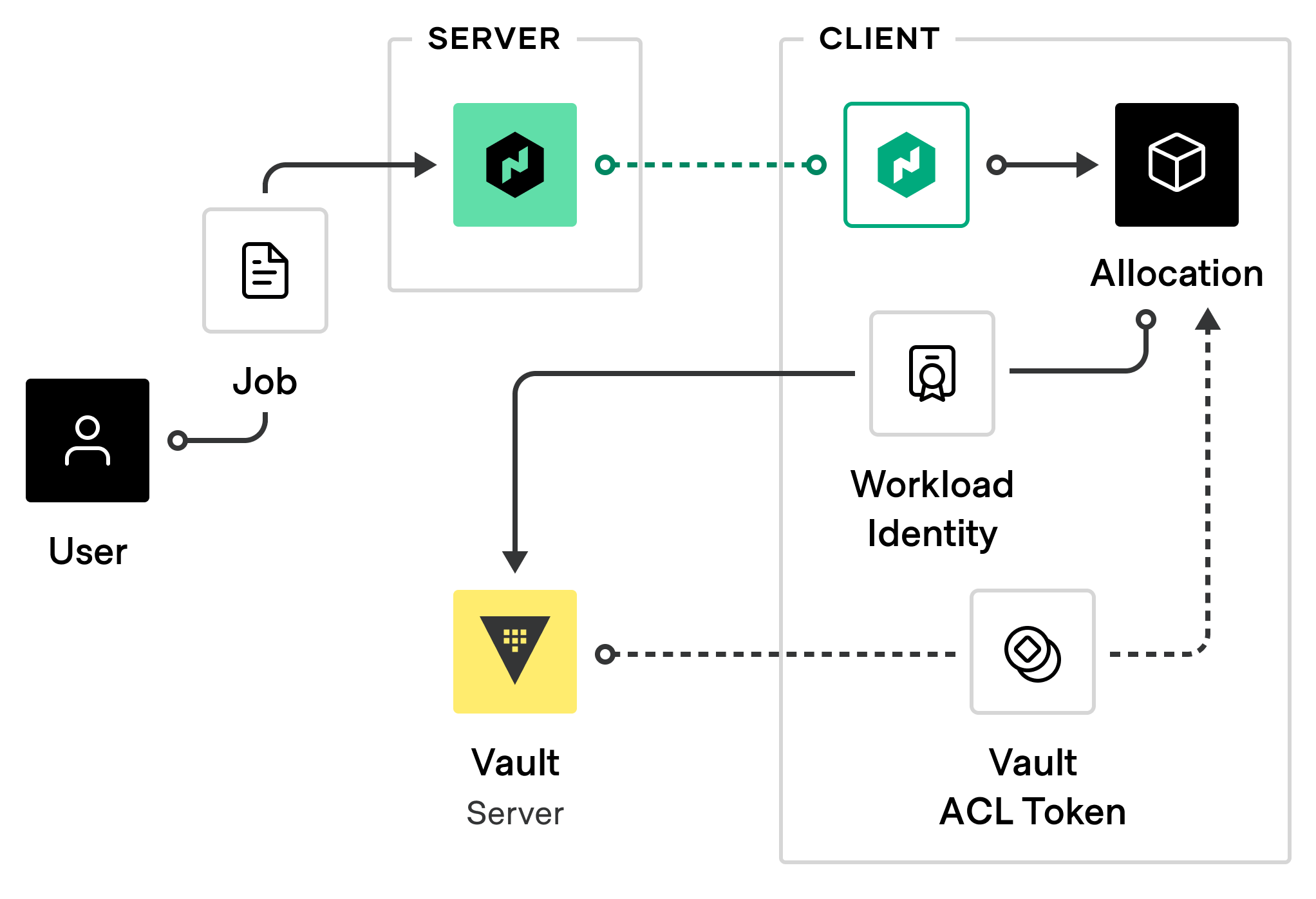
Starting in Nomad 1.7, Nomad clients can use a task's Workload Identity to authenticate to Vault and obtain a Vault ACL token specific to the task. When using Nomad workload identities, you no longer need to pass in a Vault ACL token to submit a job.
By default, Nomad only generates a workload identity for tasks that can be used
to access Nomad itself, such as for reading Variables from a template
block. To access Vault, jobs must have additional workload identities defined
as identity blocks.
To avoid having to add these additional identities to every job, you can
configure the Nomad servers with the vault.default_identity agent
configuration. Upon job registration, the Nomad servers update tasks that have
a vault block with this default identity.
You can also specify identities for Vault directly in the job. When provided,
they override the Nomad server configuration. Refer to the Workload Identities
for Vault section of the identity block
documentation for more information.
Configuring Vault Authentication
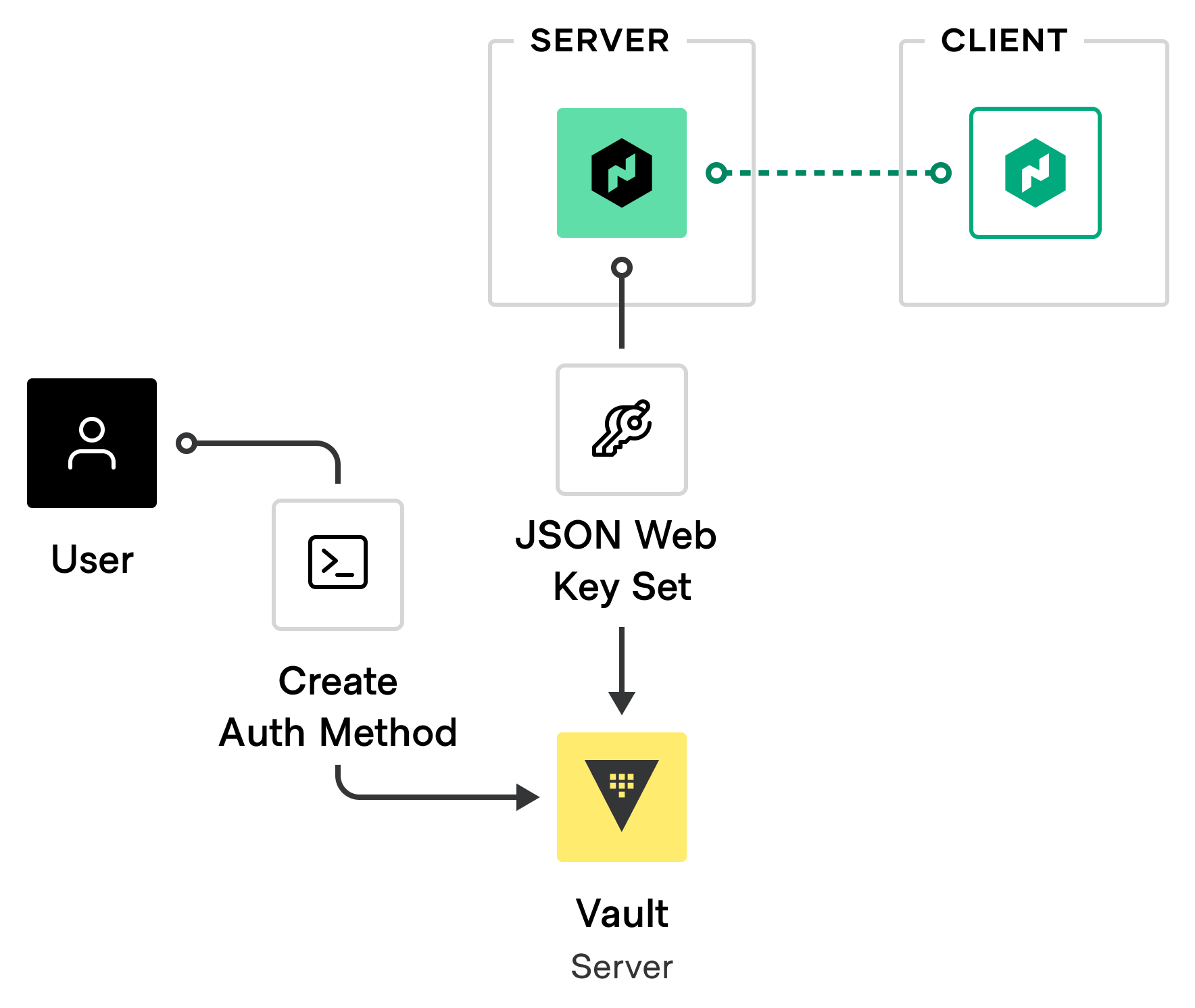
Vault must be configured to receive, validate, and trust these Nomad workload identities. Since they are encoded as JSON Web Tokens (JWTs), you must create a JWT ACL auth method. The auth method is an endpoint that Nomad can use to exchange workload identities for Vault ACL tokens.
Refer to Vault's Authentication documentation for more information.
Vault Auth Method
The auth method configuration points to Nomad's JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) URL. Vault servers call this URL to retrieve the public keys Nomad uses to sign workload identities. With these keys, Vault is able to validate their origin and confirm that they were actually created by Nomad.
The jwks_url address must be reachable by all Vault servers and should
resolve to multiple Nomad agents to avoid a single point of failure. Both Nomad
servers and clients are able to handle this request.
Refer to the Important Considerations About the JWKS
URL section for additional
information on how to configure the jwks_url value.
When an allocation that needs access access to Vault starts, the Nomad client running it exchanges the Nomad workload identities for tasks for Vault ACL tokens.
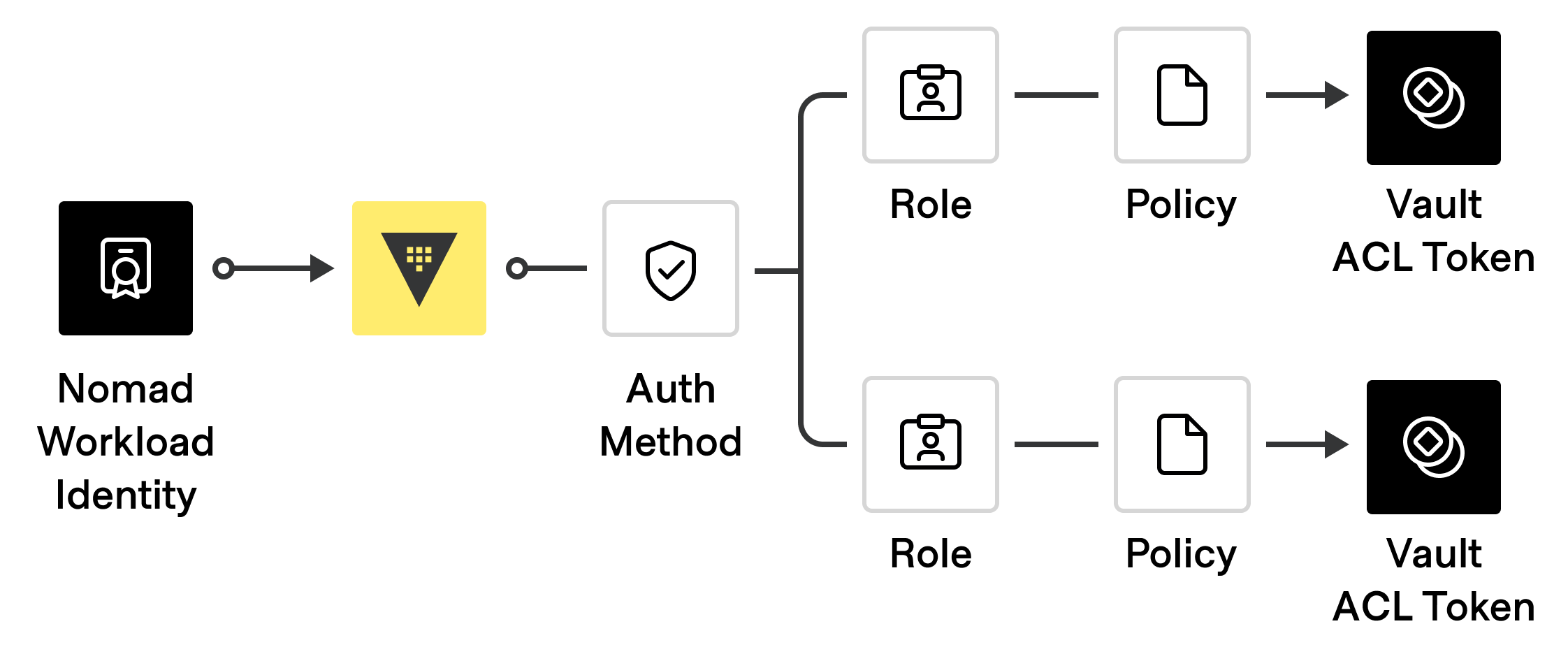
Vault ACL Role
A Vault ACL role groups multiple ACL policies to apply to a token and determine the permissions it receives.
The auth method may define a default ACL role that is applied to the ACL tokens
it generates. If no default role is set, the role must be provided in the job
using the vault.role parameter or in the Nomad client configuration
vault.create_from_role.
The ACL role specifies the list of authorized audience values using the
bound_audiences, which must have at least one match with the values
defined in the Nomad workload identity aud parameter. For security
reasons, it is recommended to only define a single audience value.
Nomad workload identities have a set of claims that can be
referenced in Vault ACL configuration. The ACL role uses the
claim_mappings parameter to determine which of these claims are made
available to the rest of the configuration.
The bound_claims parameter restricts which workload identities are able
to use the role based on their claims. Refer to Vault's Bound
Claims documentation for more information.
Vault has different types of ACL tokens. Nomad typically
uses tokens of type service since they can be renewed for as long as the
workload is active. Nomad automatically renews the Vault ACL tokens it generates
before they expire. To ensure the tokens can be renewed for as long as
necessary, token_explicit_max_ttl must be set to 0.
Alternately, you may use batch tokens. This should only be used when a secret
is requested from Vault once at the start of a task or in a short-lived prestart
task. Long-running tasks should never set allow_token_expiration=true if they
obtain Vault secrets via template blocks, as the Vault token will expire and
the template runner will continue to make failing requests to Vault until its
[vault_retry][] attempts are exhausted, at which point the task will
fail. Vault's batch tokens cannot be renewed, and Nomad will not attempt to
renew them when configured to use Workload Identity.
Vault ACL Policy
A Vault ACL role may have one or more ACL policies attached. Vault ACL policies define the permissions granted to an ACL token.
ACL policies can reference dynamic values from Nomad workload identities claims exposed from the ACL role in templated policies. The exact ACL policy rules will depend on the level of access required by tasks.
The following example ACL policy automatically grants read permissions to
secrets in the path secret/data/<job namespace>/<job name>/*, where <job
namespace> and <job name> are read from the workload identity claims
nomad_namespace and nomad_job_id.
The overall configuration structure is illustrated in the following diagram.
Vault Namespaces Enterprise
Vault Enterprise supports multiple namespaces and jobs in Nomad Enterprise can
use the vault.namespace parameter to specify which namespace to use. In a
multi-namespace environment, the authentication setup described must be applied
to each Vault namespace used by jobs.
Important Considerations About the JWKS URL
The recommended configuration assumes Vault servers are able to connect to Nomad agents (either client or servers) to retrieve the JSON Web Key Set information.
This section covers additional aspects you should consider depending on how your Vault and Nomad clusters are configured and deployed.
Mutual TLS in Nomad
It is highly recommended to use mutual TLS in production
deployments of Nomad. With mTLS enabled, the tls.verify_https_client
configuration must be set to false since it is not possible to provide client
certificates to the Vault auth method.
Alternatively, you may expose Nomad's JWKS URL from a proxy or a load balancer that handles the mutual TLS connection to Nomad and exposes the JWKS URL endpoint over standard TLS.
Vault Servers Not Able to Connect to Nomad
If the Vault servers are not able to reach Nomad's JWKS URL, you may read the
public keys from Nomad's /.well-known/jwks.json endpoint
and provide them to the auth method directly using the
jwt_validation_pubkeys parameter. The keys must be converted from JWKS to
PEM format.
You may also host the JWKS JSON response from Nomad in an external location
that is reachable by the Vault servers, and use that address as the value for
jwks_url.
It is important to remember that the Nomad keys are rotated periodically,
so both approaches should be automated and done continually. The rotation
frequency is controlled by the server.root_key_rotation_threshold
configuration of the Nomad servers.
Additional References
The Vault ACL with Nomad Workload Identities tutorial provides guided instructions on how to configure Vault and Nomad for workload identities.
The nomad setup vault command and the
hashicorp-modules/nomad-setup/vault Terraform
module can help you automate the process of applying configuration to a Vault
cluster.
Authentication Without Workload Identity (Legacy)
To use the legacy Vault integration, Nomad servers must be provided a Vault token. This token can either be a root token or a periodic token with permissions to create from a token role. The root token is the easiest way to get started, but we recommend a token role based token for production installations. Nomad servers will renew the token automatically. Note that the Nomad clients do not need to be provided with a Vault token.
Deprecation Warning
This legacy workflow will be removed in Nomad 1.9. Before upgrading to Nomad 1.9 you will need to have configured authentication with Vault as described in Nomad Workload Identities.
See the Enterprise specific section for configuring Vault Enterprise.
Root Token Integration
If Nomad is given a root token, no further configuration is needed as Nomad can derive a token for jobs using any Vault policies. Best practices recommend using a periodic token with the minimal permissions necessary instead of providing Nomad the root vault token.
Token Role based Integration
Vault's Token Authentication Backend supports a concept called "roles". Token roles allow policies to be grouped together and token creation to be delegated to a trusted service such as Nomad. By creating a token role, the set of policies that tasks managed by Nomad can access may be limited compared to giving Nomad a root token. Token roles allow both allowlist and denylist management of policies accessible to the role.
To configure Nomad and Vault to create tokens against a role, the following must occur:
Create a "nomad-server" policy used by Nomad to create and manage tokens.
Create a Vault token role with the configuration described below.
Configure Nomad to use the created token role.
Give Nomad servers a periodic token with the "nomad-server" policy created above.
Required Vault Policies
The token Nomad receives must have the capabilities listed below. An explanation for the use of each capability is given.
The above nomad-server policy is
available for download. Below is an example of writing this policy to Vault:
Vault Token Role Configuration
A Vault token role must be created for use by Nomad. The token role can be used
to manage what Vault policies are accessible by jobs submitted to Nomad. The
policies can be managed as a allowlist by using allowed_policies in the token
role definition or as a denylist by using disallowed_policies.
If using allowed_policies, tasks may only request Vault policies that are in
the list. If disallowed_policies is used, task may request any policy that is
not in the disallowed_policies list. There are trade-offs to both approaches
but generally it is easier to use the denylist approach and add policies that
you would not like tasks to have access to into the disallowed_policies list.
An example token role definition is given below:
Token Role Requirements
Nomad checks that token role has an appropriate configuration for use by the cluster. Fields that are checked are documented below as well as descriptions of the important fields. See Vault's Token Authentication Backend documentation for all possible fields and more complete documentation.
allowed_policies- Specifies the list of allowed policies as a comma-separated string. This list should contain all policies that jobs running under Nomad should have access to.disallowed_policies- Specifies the list of disallowed policies as a comma-separated string. This list should contain all policies that jobs running under Nomad should not have access to. The policy created above that grants Nomad the ability to generate tokens from the token role should be included in list of disallowed policies. This prevents tokens created by Nomad from generating new tokens with different policies than those granted by Nomad.A regression occurred in Vault 0.6.4 when validating token creation using a token role with
disallowed_policiessuch that it is not usable with Nomad. This was remedied in 0.6.5 and does not effect earlier versions of Vault.token_explicit_max_ttl- Specifies the max TTL of a token. Must be set to0to allow periodic tokens.name- Specifies the name of the policy. We recommend using the namenomad-cluster. If a different name is chosen, replace the token role in the above policy.orphan- Specifies whether tokens created against this token role will be orphaned and have no parents. Nomad does not enforce the value of this field but understanding the implications of each value is important.If set to false, all tokens will be revoked when the Vault token given to Nomad expires. This makes it easy to revoke all tokens generated by Nomad but forces all Nomad servers to use the same Vault token, even through upgrades of Nomad servers. If the Vault token that was given to Nomad and used to generate a tasks token expires, the token used by the task will also be revoked which is not ideal.
When set to true, the tokens generated for tasks will not be revoked when Nomad's token is revoked. However Nomad will still revoke tokens when the allocation is no longer running, minimizing the lifetime of any task's token. With orphaned enabled, each Nomad server may also use a unique Vault token, making bootstrapping and upgrading simpler. As such, setting
orphan = trueis the recommended setting.token_period- Specifies the length the TTL is extended by each renewal in seconds. It is suggested to set this value on the order of magnitude of 3 days (259200 seconds) to avoid a large renewal request rate to Vault. Must be set to a positive value.renewable- Specifies whether created tokens are renewable. This allows Nomad to renew tokens for tasks. Nomad clients will automatically detect when tokens cannot be renewed and will not attempt to renew them (seevault.allow_token_expiration).
The above nomad-cluster token role is
available for download. Below is an example of writing this role to Vault:
Example Configuration
To make getting started easy, the basic nomad-server
policy and
nomad-cluster role described above are
available for download.
The below example assumes Vault is accessible, unsealed and the operator has appropriate permissions.
Retrieving the Token Role based Token
After the token role is created, a token suitable for the Nomad servers may be retrieved by issuing the following Vault command:
The -orphan flag is included when generating the Nomad server token above to
prevent revocation of the token when its parent expires. Vault typically
creates tokens with a parent-child relationship. When an ancestor token is
revoked, all of its descendant tokens and their associated leases are revoked
as well.
When generating Nomad's Vault token, we need to ensure that revocation of the
parent token does not revoke Nomad's token. To prevent this behavior we
specify the -orphan flag when we create the Nomad's Vault token. All
other tokens generated by Nomad for jobs will be generated using the policy
default of orphan = false.
More information about creating orphan tokens can be found in Vault's Token Hierarchies and Orphan Tokens documentation.
The -period flag is required to allow the automatic renewal of the token. If this is left out, a vault token renew command will need to be run manually to renew the token.
The token can then be set in the server configuration's
vault block, as a command-line flag, or via an environment
variable.
An example of what may be contained in the configuration is shown below. For complete documentation please see the Nomad agent Vault integration configuration.
Troubleshooting Legacy Authentication
Invalid Vault token
Upon startup, Nomad will attempt to connect to the specified Vault server. Nomad will lookup the passed token and if the token is from a token role, the token role will be validated. Nomad will not shutdown if given an invalid Vault token, but will log the reasons the token is invalid and disable Vault integration.
No Secret Exists
Vault has two APIs for secrets, v1 and v2. Each version
has different paths, and Nomad does not abstract this for you. As such you will
need to specify the path as reflected by Vault's HTTP API, rather than the path
used in the vault kv command.
You can see examples of v1 and v2 syntax in the
template documentation.
Enterprise Configuration
This feature requires Nomad Enterprise(opens in new tab).
Nomad Enterprise allows jobs to use multiple Vault Namespaces. There are a few configuration settings to consider when using this functionality.
Example Configuration
Below is an example for creating two Namespaces within Vault.
Required Vault Policies
Policies are configured per Vault namespace. We will apply the policy in the example above to each namespace—engineering and engineering/frontend.
We will also configure the previously configured nomad-workloads role with each
Namespace
The Nomad agent Vault integration configuration supports specifying a Vault Namespace, but since we will be using multiple it can be left blank. By default Nomad will interact with Vault's root Namespace, but individual jobs may specify other Vault Namespaces to use.
For legacy authentication, the same steps can be taken to inject a Vault token from the Retrieving the Token Role based Token steps.
Submitting a job with a Vault Namespace
The example job file below specifies to use the engineering Namespace in
Vault. It will authenticate to Vault using its workload identity with the
nomad-workloads Vault role, then read the value at secret/foo and fetch the
value for key bar.
Submitting a job with a Vault Namespace with Legacy Authentication
For the legacy authentication, because allow_unauthenticated
is set to false job submitters will need to provide a sufficiently privileged
token when submitting a job. A token that has access to an appropriate policy in
engineering namespace is needed:
The token can then be submitted with our job
Migrating to Using Workload Identity with Vault
Migrating from the legacy (pre-1.7) workflow where workloads use the agent's Vault token requires configuration on your Vault cluster and your Nomad server agents. It does not require updating your running Nomad jobs unless you wish to specify a non-default role. To migrate:
- Create the Vault auth method, default role, and policies on your Vault cluster.
- Enable
vault.default_identityblocks in your Nomad server agent configurations, but do not modify any of the existing Vault configuration. - Upgrade your cluster following the documented Upgrade Process.
- Resubmit Nomad jobs that need access to Vault to redeploy them with a new
workload identity for Vault.
- (Optionally) Add
vault.rolefields to any Nomad jobs that will not use the default role. - (Optionally) add
identityblocks to your jobs if you want to use a different identity because of how your auth method and roles are configured.
- (Optionally) Add
- Once all jobs have been resubmitted, you may remove parameters no longer used
by the Nomad server agents from the
vaultconfiguration block.